June 04, 2023
4 min read
Gestalt Principles For Data Science
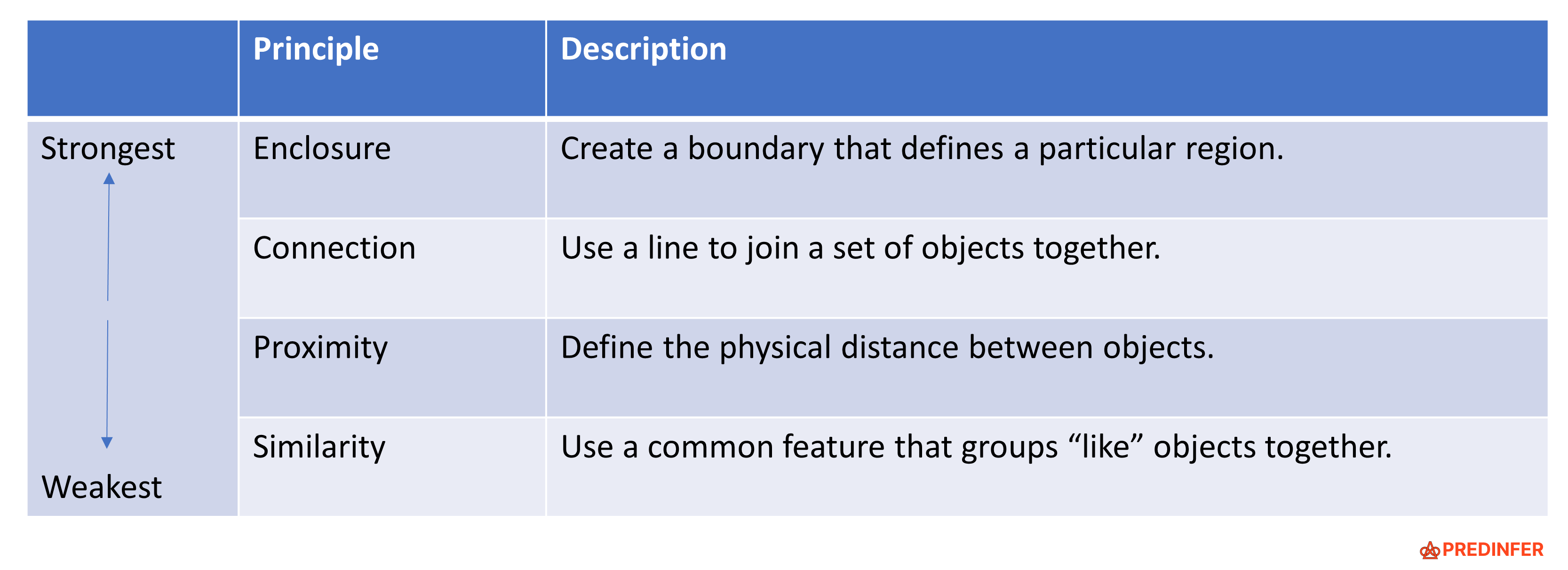
Gestalt is a German word which means shape or form. They are a set of principles used to visually group objects. The Gestalt principles of "Enclosure", "Connection", "Proximity" & "Similarity" come from a branch of psychology that determine how we humans visually perceive the grouping of objects.
Gestalt principles can be ranked in order of strongest influence to weakest influence as follows i.e.
Enclosure > Connection > Proximity > Similarity
Similarity
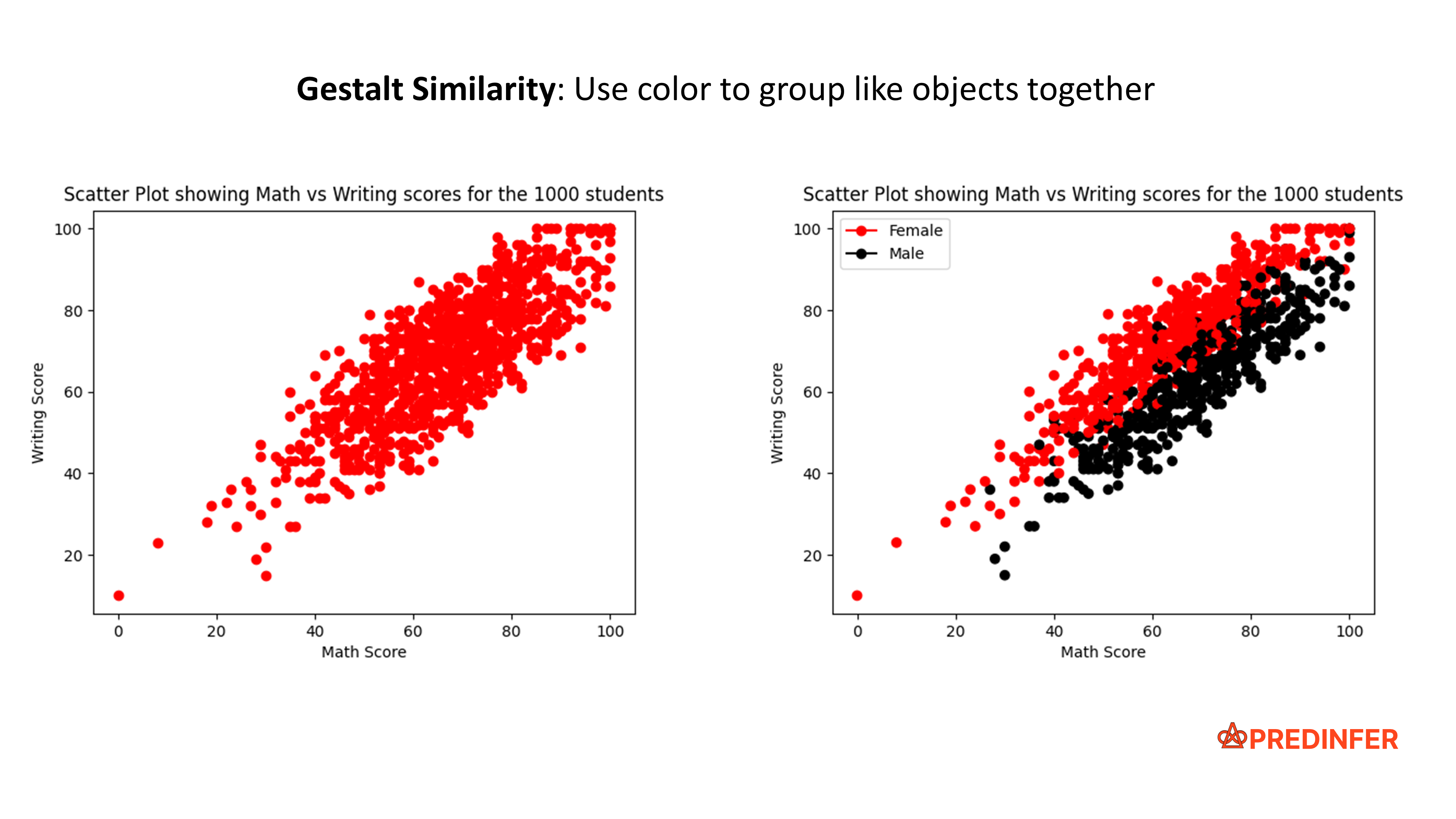
The similarity principle uses a common feature such as Shape or Color to group like objects together.
In the following generic example, take a moment to closely observe how "Shape" and "Color" are used to create two groups.


As you can see from the last example, the use of shape and color together increases the emphasis on showing that there are two distinct groups here.
Proximity
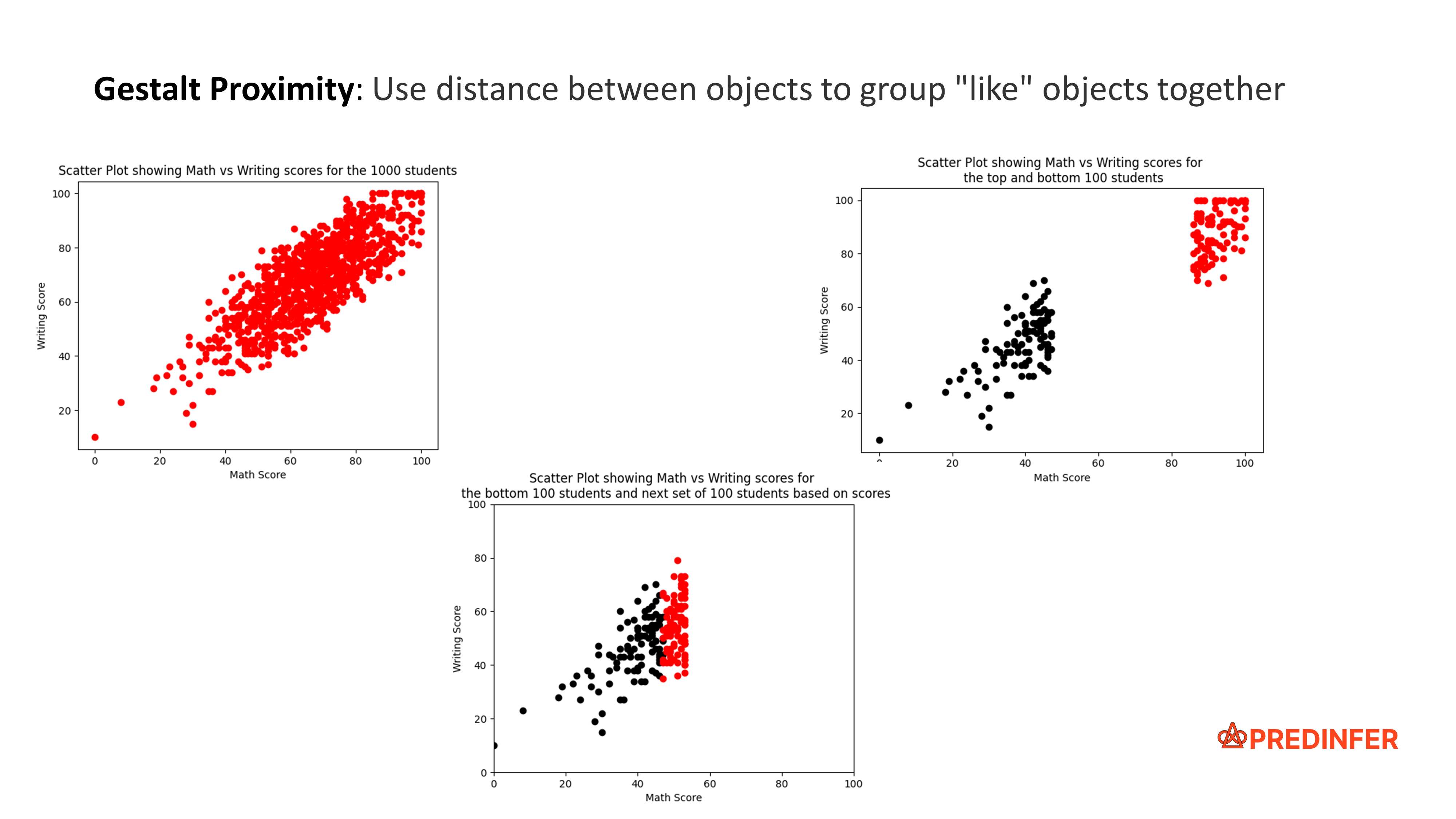
The proximity principle uses distance between objects to group "like" objects together. In 2D space, this can be considered as the distance of separation on the X-Axis vs Y-Axis.
In the following example, observe how distance between objects is used to create two distinct groups.
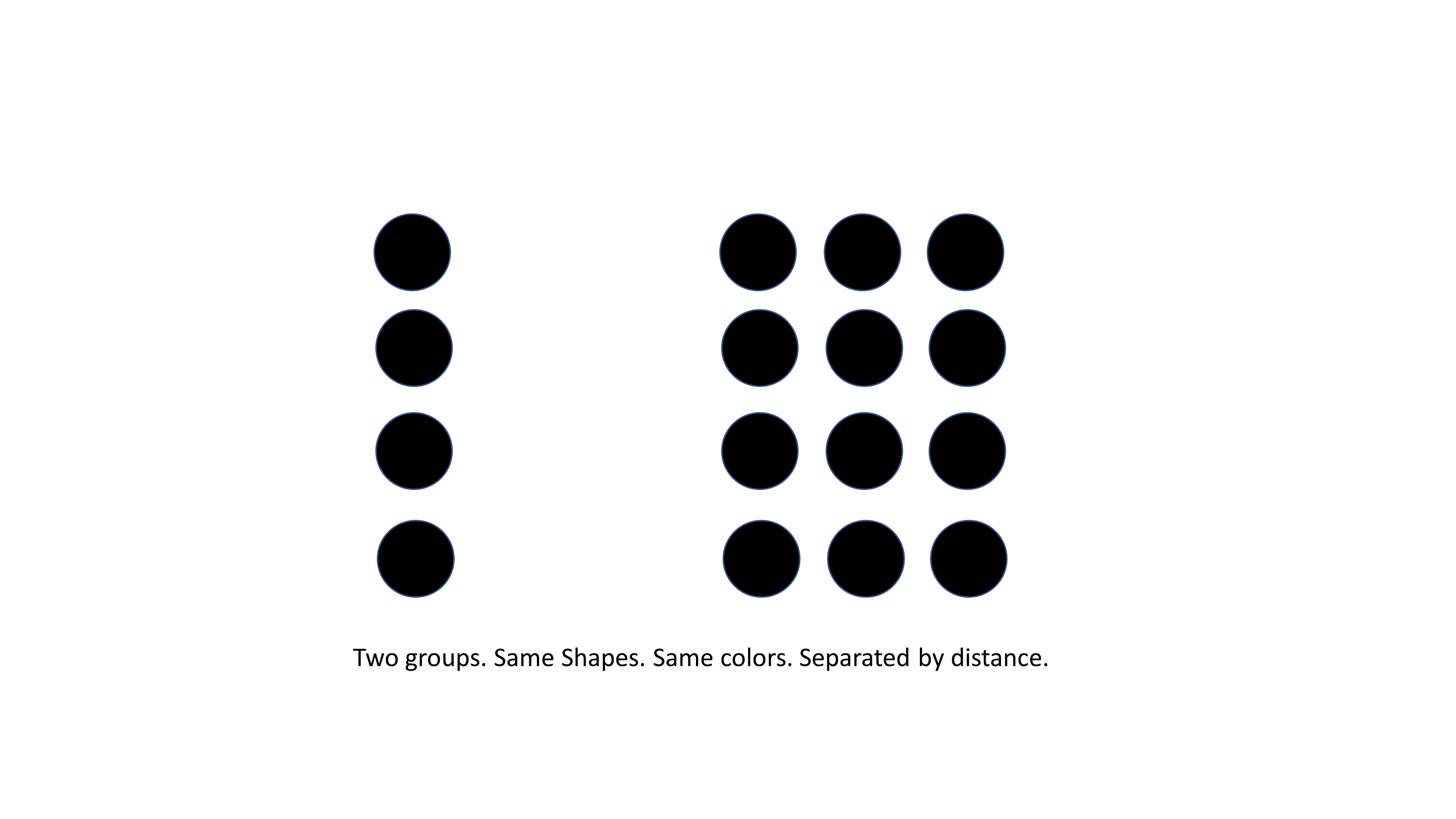
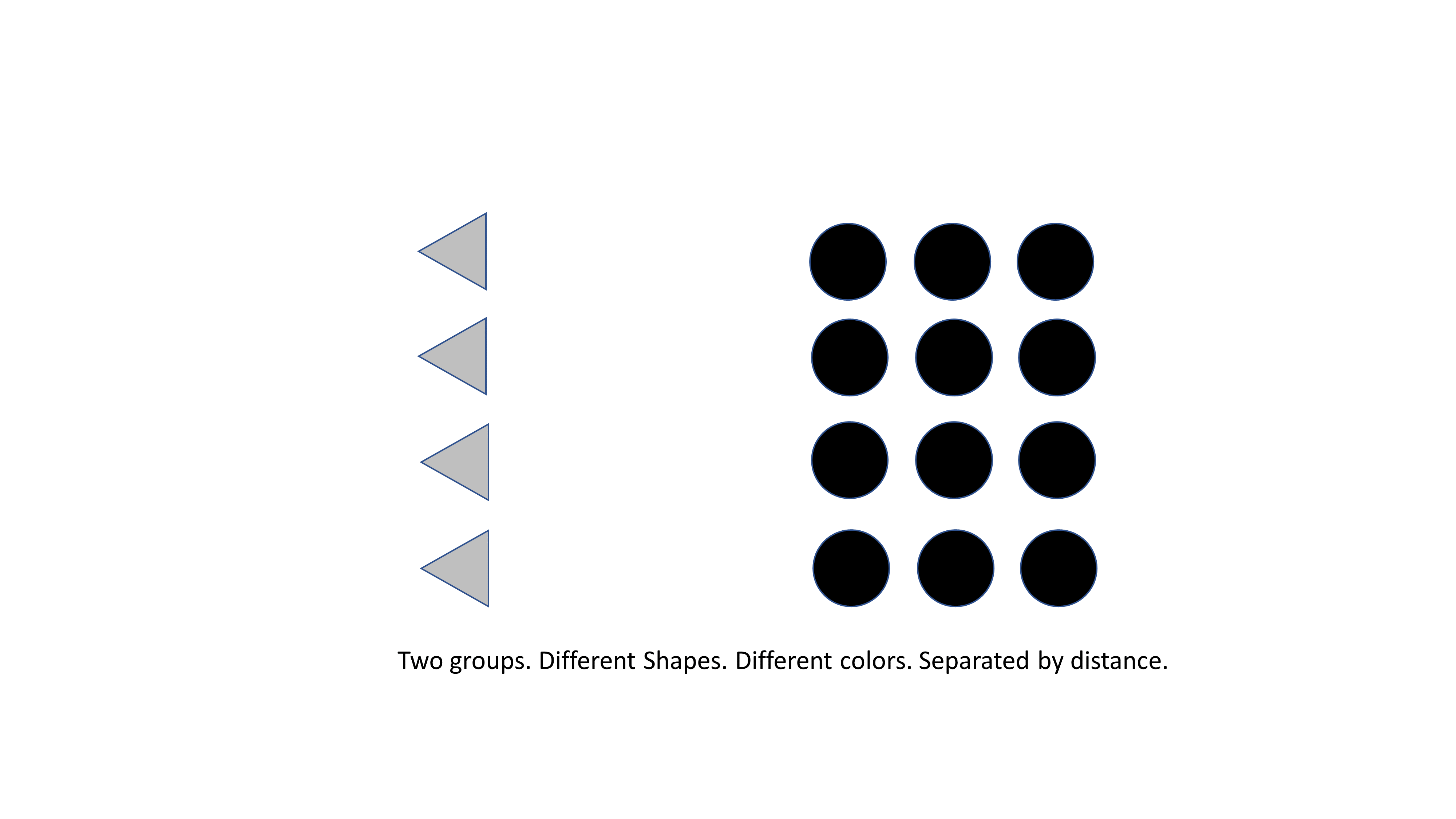
In the following example, notice how the use of the similarity principle (use of different shape and color) along with the proximity principle (distance between objects) further amplifies the distinction between the two groups.
Connection
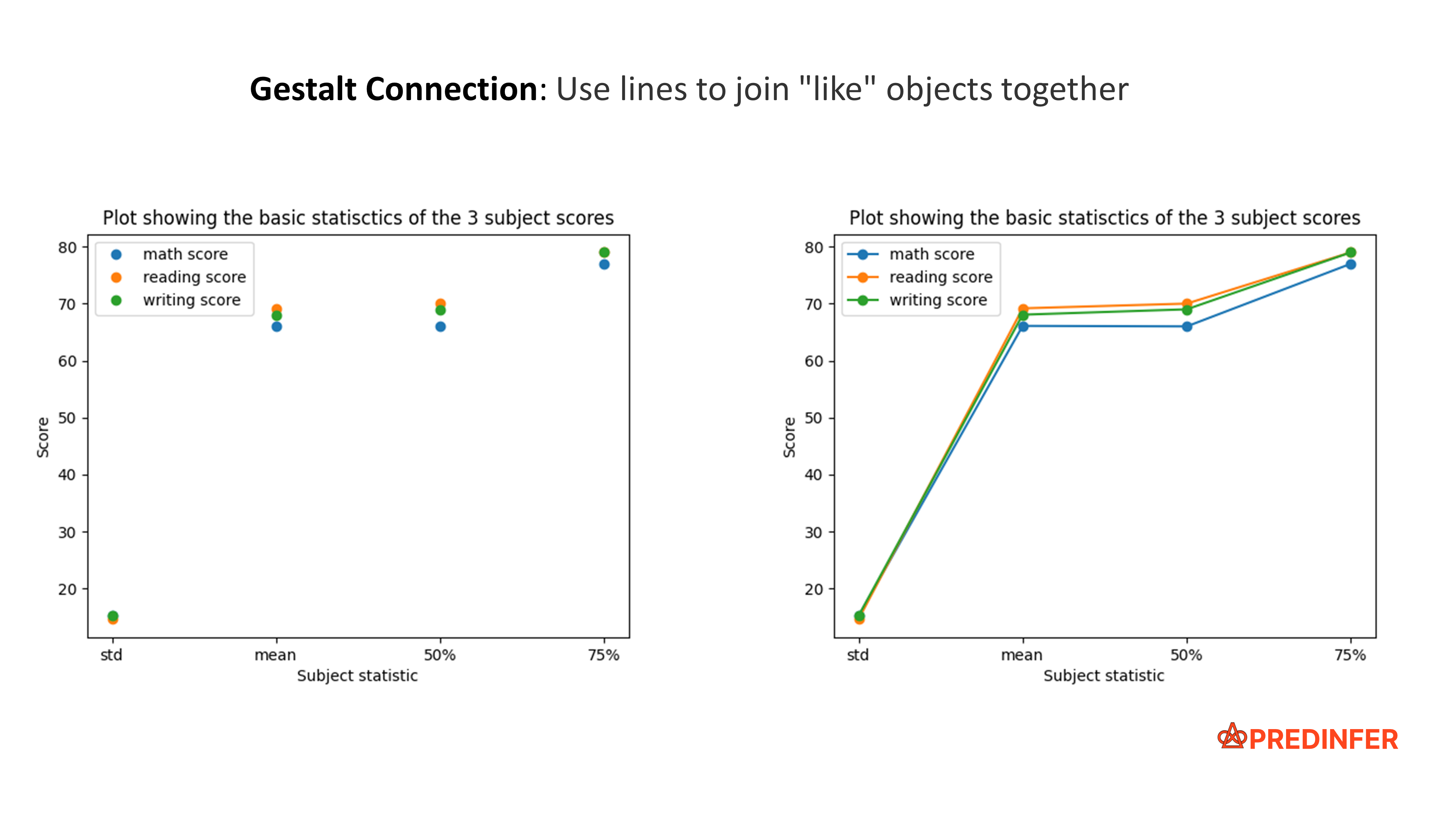
The connection principle joins "like" objects together (most often with lines). In 2D space, a line chart is a common example of using this principle.
In the following example, observe how an arrow connecting objects is used to create four distinct groups.

Enclosure
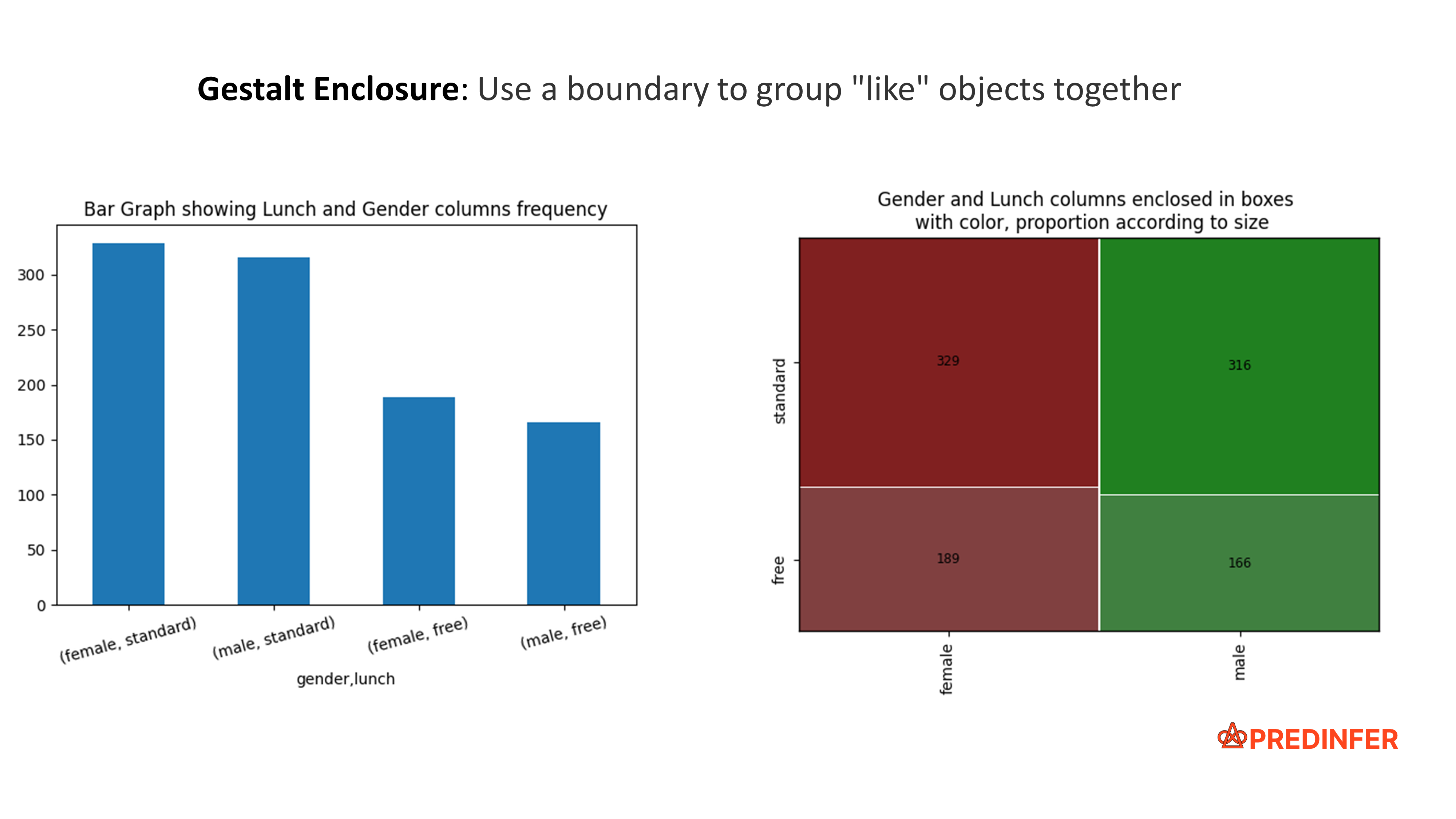
The enclosure principle is the strongest of all the Gestalt principles i.e. our mind prioritizes this principle over all others. With this principle, you create a boundary that groups "like" objects together within a bounded region.
In the following example, all four Gestalt principles are used as follows:
- Similarity - all objects are circles but one group of circles have a different color.
- Proximity - one group of objects are physically separated from all other groups.
- Connection - two objects in different groups are joined with a line.
- Enclosure - two bounded boxes are used.
But as you can see, there are still only two groups that the mind distinctly identifies based on the two bounded boxes from the use of the enclosure principle.
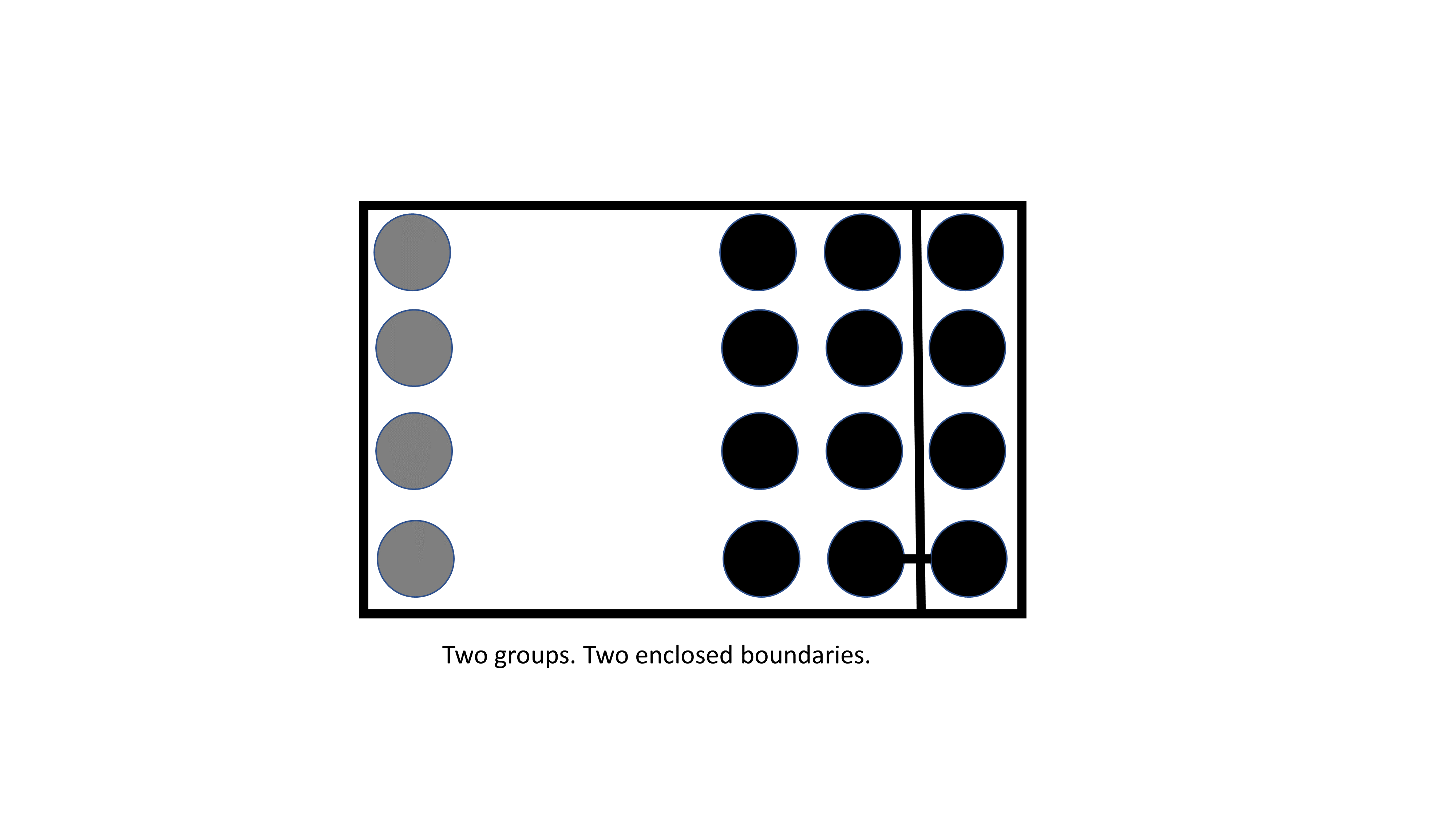
For a more real world example, let's look at how we can apply the above Gestalt principles to a dataset consisting of Math, Writing & Reading scores for 1000 students. For the source code of the examples below, see our GitHub repository.
Similarity

Proximity
Connection
Enclosure
With the second plot below, notice how it is easier to visually analyze the data. For example:
- There are 518 female students (indicated by the red color) while the rest are male students (indicated by the green color).
- It is easier to notice categories like "189 female students with free lunch".
- The proportion of students in each category relative to the total number of students is also easily identified (notice difference in size & color of each of the four categories).
So the next time you are working on a PowerPoint presentation or creating graphs for your Data Science project, consider how you can incorporate these Gestalt Principles to improve the visual design of your work.